|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| About Mauritania | |||||||||
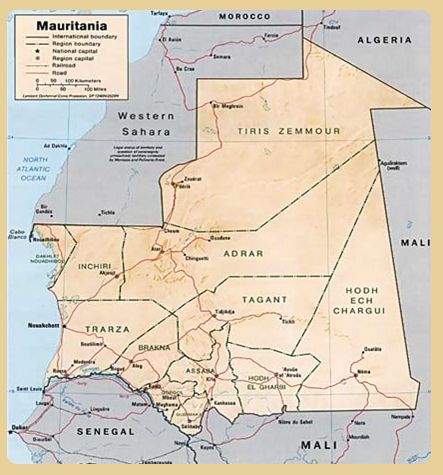
Official Name: Islamic Republic of Mauritania. President: Mohamed OULD ABDEL AZIZ (elected July 18, 2009). Prime Minister: Moulaye OULD MOHAMED LAGHDAF (appointed 11 August 2009). 2. GEOGRAPHIC DATA: Area: 1,030,700 km 2 (France: 675,417 sq km). Capital: Nouakchott. Major cities: Nouadhibou, Ka¨¦di, Rosso, Zouerate, Atar. Official language: Arabic. Languages: Arabic, Pulaar, Soninke, and Wolof. Currency: Ouguiya (1 € = 360 UM approximately). National Day: November 28 (Independence in 1960). 3. DEMOGRAPHICS: Population: 3,200,000 inhabitants. Density: 2.2 people / km 2. Population growth: 2.5% (World Bank 2008). Life expectancy: 64 years. Literacy rate: 56% (UNICEF, 2008). Religion: Islam (official religion). 4. ECONOMIC DATA: GDP (2008): $ 2.86 billion (World Bank). GDP per capita (2008): $ 1,042 (IMF). Growth Rate (2007): 1.9% (World Bank). Budget 2009: UM 227.56 billion (about $ 866 million). Trade Balance (2008): + $ 454 million. Main clients (2008): China (54.5%), France (14.3%), Spain (P, 8%), Italy (9.6%) - source EIU. Major suppliers (2008): France (23.5%), China (12.1%), Netherlands (9%), Spain (8.4%) - source EIU. Share of major sectors in GDP: - Agriculture: 12.5%. - Industry: 46.7%. - Services: 40.7%. 5. GEOGRAPHIC PRESENTATION: Located in the Western Desert, between 15th and 17th degrees of north latitude, the 5 and 7th degrees west longitude, Mauritania is bounded on the west by the Atlantic Ocean, south by Senegal, with the east and southeast by Mali, on the north by Algeria and northwest by Western Sahara. Mauritania is par excellence the country's most arid Sahel (desert more than 75%) and largest with an area of 1,030,700 sq. km. This country has two seasons: - A rainy season characterized by three to five months of erratic and poorly distributed rainfall; - A very short cold season. 6. POPULATION: The population of Mauritania has experienced a similar trend to that of other countries of the Sahel region. It rose, according to national statistical services of 1,864,236 to 2,218,542 between 1988 to 1994, representing a growth of 2.9% for this period. This was due to demographic parameters of the underdeveloped countries (very high birth rate), improvement of health conditions; the existence of religious and socio-cultural considerations, including early marriage, polygamy and Family planning is still limited. The average density is about 2.2 inhabitants per km 2. 7. ECONOMIC RESOURCES OF THE COUNTRY: Mauritania's economy is based primarily on the potential resources of the various sub sectors below: - The soil resources (agriculture, livestock, forest) whose valuation is severely hampered by harsh climatic constraints. - The resources of the sea are very important with regard to fish stocks and species of economic interest (pelagic fish, bottom fish) by the size of the continental shelf. The development of the latter was taken over by the Mauritanian very recently with promising results (nearly 600,000 tons in 1988). Stocks are permissible of 1,200,000 tonnes for pelagic fish and 50,000 tonnes for groundfish. - The resources of the subsoil, especially mining, are the main exports of Mauritania. These resources are subject to fluctuations in world currency. 8. MAJOR AREAS OF AGRO-CLIMATE COUNTRY: The consequences (climate, physical, human and economic) of desertification identified nationally, are a major concern for development and protection of natural resources within the four eco-climatic zones as follows: - Arid zone; - Sahelian zone; - The area of the river; - The coastline. Arid Zone, the largest ecological unit in the country, includes different entities under one another, with biogenetic resources scarce and scattered, localized in very specific areas. The main problems relate to the protection against sand oasis, towns, water points and hydraulic structures (small areas of recession) and the fight against water erosion caused by torrential floods in wadis. MAURITANIAN CULTURE: Introduction: Culture of Mauritania, by the country's geographical position, is a blend of Moorish cultures (Arab-Berber) and Negro-African. Mauritania has long been a place of convergence of various streams of Civilization (empires of Mali, Ghana, the Almoravids, etc...) that have succeeded and made Mauritania fertile land exchanges and ethnic and cultural intermingling as rich and varied. The historic towns of Chinguetti, Adrar in Tichitt and Oualata, classified by UNESCO as World Heritage of Humanity, are a visible expression of this heritage and diversity that have marked the history of Mauritania. Islam, religion of the State and People, is the true cement of Mauritanian society. Maliki rite of Sunni Islam practiced in the country is a religion of openness and tolerance. The universities of the Desert (known locally as traditional universities or Mahadras Dudde) and its ancient libraries, where sleep for centuries many thousands of unpublished manuscripts, representing the richness and originality of the cultural heritage of Mauritania. The country is known for its poets whose aura was far beyond the borders of the country and the sub-region. Do not we say that Mauritania is "the country of a million poets"? Mauritanian scholars in theology, causing the spread of Islam in Black Africa (Western in particular) have a great reputation in the Arab and Muslim worlds, where they teach the subject in various universities. Mauritanian social life often takes place around the traditional mint tea. Music: The music is pervasive in Mauritanian culture. It was inspired by the Maghreb and black  Africa. This music can express different feelings; tell stories and local legends or religious. One can hear it in the tourist and cultural sites but also at festivals or travel in the country. Traditional music is sung in different languages of the country: Arabic, Pulaar, Soninke and Wolof. Africa. This music can express different feelings; tell stories and local legends or religious. One can hear it in the tourist and cultural sites but also at festivals or travel in the country. Traditional music is sung in different languages of the country: Arabic, Pulaar, Soninke and Wolof.The main instruments of traditional music are: - The Ardin, instrument played by the Moorish women. - The djembe, percussion instrument can have different sizes and shapes. It is made of wood and goat skin or camel. - The hoddu, very close to the "Tidinite" is an instrument of many strings connecting a sounding board and an oval shaped wooden shaft, which is played by "wambaab¨¦s" in the river valley. - The "tidinite", another stringed instrument played by griots Moors, is a kind of guitar-specific sub-region. - The "tbel" big drum used musical instruments and traditional means of gathering, warning or alert. In Mauritania, the custom is that only Iggawen, descendants of the families of griots, can sing or play musical instruments in public spectacles.  Clothing: The traditional male robe (Derraa) is cotton blue or white to mitigate the hot temperatures often in the country. In the more affluent, it is crafted in fabric colored with different colors of embroidery multifaceted. The haouli is a rectangular piece of fabric needed in the desert that goes around the head or shoulders to protect against wind and sun. The serwal worn under the robe for men, baggy pants that are breathable. The Moorish women drape themselves in veils (melehfa) in colorful fabrics. The women of the valley are, in turn, a headscarf and colorful tunics under which they wear loincloths.  Cuisine:  The kitchen was the domain of women, which, thanks to the fertility of their imaginations, invented many dishes and variations on traditional recipes. By region, we find the following dishes: The kitchen was the domain of women, which, thanks to the fertility of their imaginations, invented many dishes and variations on traditional recipes. By region, we find the following dishes:- Al-kecra, a sort of cake, flour, wheat or barley, baked or in sand preheated to embers; - Al-'aich: thick porridge of millet flour, barley or wheat; - Abragat: millet gruel and cherkach (watermelon seeds); - Cherchem: millet, wheat or barley boiled without being crushed in advance; - Mbellakh: millet, wheat, barley or rice cooked in chopped meat broth; - Lacciri (lathiri): fine couscous prepared from sorghum flour, millet and rice we eat well watered, a choice of tomato sauce to meat to fish in bean leaves (Haako) or vegetables. It can also be eaten with fresh milk or curd; - Thieboudienne: form of rice and fish which is a sub-regional dish; - Maru: rice with dried fish (guedj or smoked) or meat with vegetables or white beans; - Benafer: stew meat or chicken with potatoes and pickled onions; - Firire: fish fried in an oil bath and served with a spicy tomato sauce often; - Karaw ou Fond¨¦: boiled rather light, made of large grains of couscous sorghum or millet served with milk; - Laax (lakh): kind of slurry or A'ishah prepared as Karawa but thicker; - Couscous with millet flour, wheat, barley. It is the main dish in most areas of the country; - Various kinds of grilled meats (meat, fish, poultry...); - Al Lamb barbecue: meat cooked in the sand (hofra, home) over hot coals or on skewers. Mauritanian cuisine is very rich and varied because of the influence of Arab and African cultures that intersect in the country. |
|||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|